The Mandelbrot set was a hot subject of computer art in the 1980s. The algorithm is quite simple:
- For each point on the screen, do an iterative calculation and decide whether the calculation diverges or not.
- Color that spot on the screen according to how many iterations it took to diverge or brown if it didn’t diverge in 1000 iterations.
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
int m = 2048; /* Image x - dimension */
int n = 2048; /* Image y - dimension */
double lim = 4.0; /* Limit to determine convergence */
int count_max = 1000; /* maximum number of iterations */
/* Region of interest */
double x_max = 1.25;
double x_min = -2.25;
double y_max = 1.75;
double y_min = -1.75;
struct timespec ts_start, ts_end;
float time_total;
int i, j, k;
FILE *output_unit;
int **count;
double x, x1, x2, y, y1, y2;
count = (int **)malloc(m * sizeof(int *));
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
count[i] = malloc(n * sizeof(int));
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &ts_start);
/* Carry out the iteration for each pixel, determining the number */
/* of iterations required for the new point (x2,y2) to move away */
/* from the original point (x,y) by the predefined distance (limit) */
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
y = ((i - 1) * y_max + (m - i) * y_min) / (m - 1);
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
x = ((j - 1) * x_max + (n - j) * x_min) / (n - 1);
count[i][j] = 0;
x1 = x;
y1 = y;
/* Loop checking convergence */
k=0;
while ((k++ < count_max) && (x1*x1 + y1*y1 < lim))
{
x2 = x1 * x1 - y1 * y1 + x;
y2 = 2 * x1 * y1 + y;
x1 = x2;
y1 = y2;
}
count[i][j] = k;
}
}
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &ts_end);
time_total = (ts_end.tv_sec - ts_start.tv_sec) * 1e9 + (ts_end.tv_nsec - ts_start.tv_nsec);
printf("\nTotal time is %f ms", time_total / 1e6);
/* Write data to a binary file for visualization with paraview */
char *output_filename = "mandel_2048x2048_int.raw";
output_unit = fopen(output_filename, "wb");
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
fwrite(count[j], m * sizeof(int), 1, output_unit);
fclose(output_unit);
}
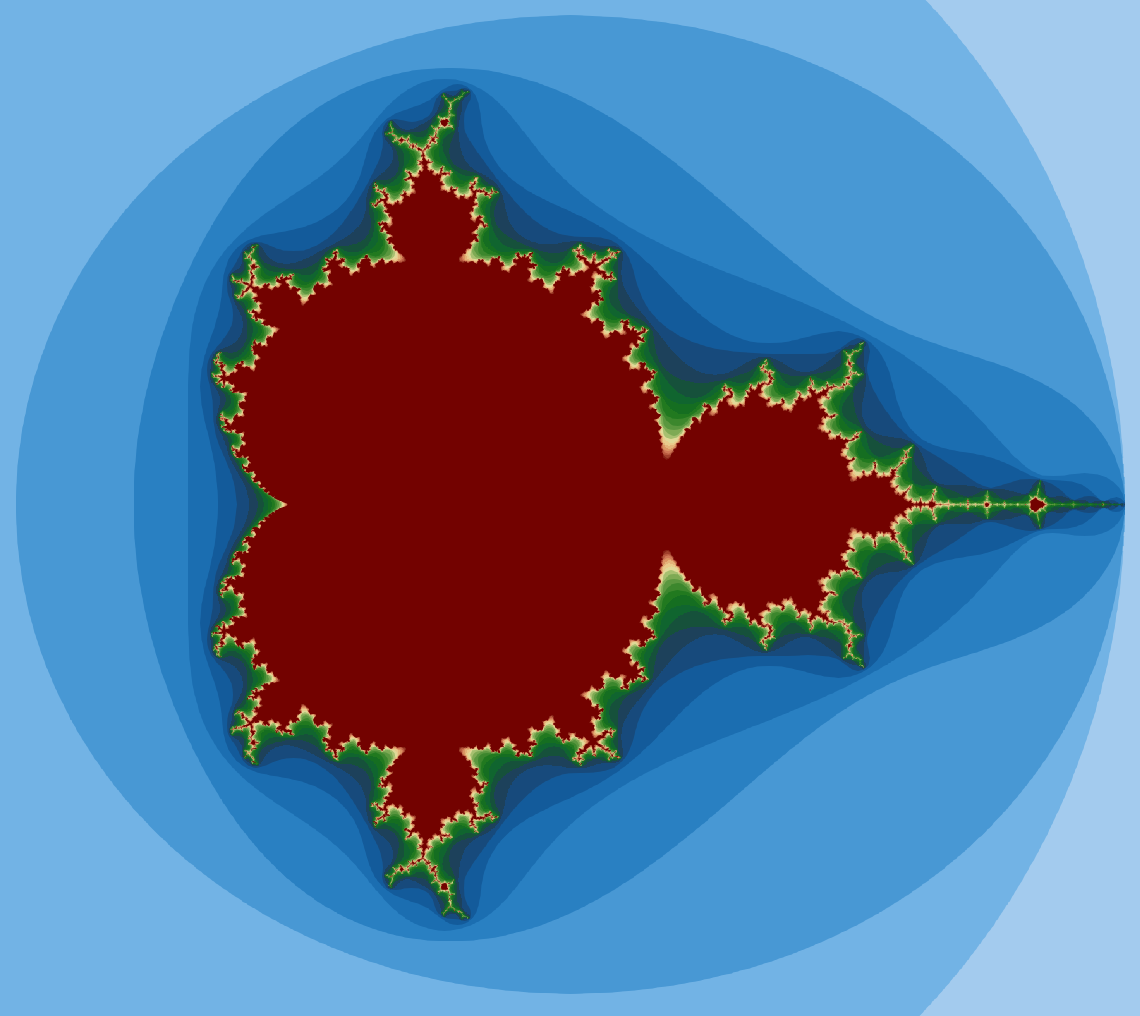
Calculation result visualized with paraview.
- First, compile and run the program without OpenMP.
- Note how long it took to run. A millisecond is not enough to get good performance measurements on.
- Next, increase the dimensions
m,nto3000,3000and recompile. Check the run time.
Now comes the parallelization.
Parallelize the Mandelbrot Code
- Decide what variable or variables should be made private, and then compile and test the code.
- Run on few different numbers of CPUs. How does the performance scale?
- Try different scheduling types. How does it affect the performance? What seems to work best for this problem?
Solution
#pragma omp parallel for private (i,j,k,x,x1,x2,y,y1,y2) schedule(dynamic)